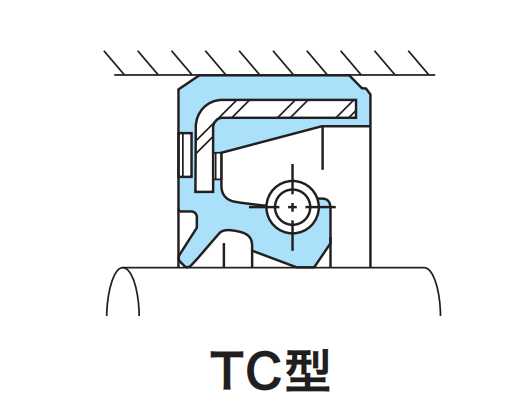
In the field of industrial rotary shaft sealing, the double-lip oil seal (featuring a main sealing lip energized by a garter spring, a secondary dust lip, and a stainless steel casing) is a classic, reliable, and widely used sealing solution. Its design ingeniously integrates multiple key elements to address sealing challenges in complex operating conditions. This article provides an in-depth analysis of its structural advantages, core component functions, material selection, and typical applications.
I. Structural Advantages & Functions of Core Components
-
Stainless Steel Casing: The Rigid Foundation
- Function: Acts as the "backbone," providing a rigid support structure to ensure overall dimensional stability and resistance to deformation during installation and use.
- Advantages:
- High Strength & Rigidity: Withstands installation forces, shaft eccentricity, and system pressure, preventing seal distortion.
- Dimensional Stability: Ensures a tight, stable fit (interference fit) between the seal OD and the housing bore, providing reliable static sealing.
- Enhanced Durability & Longevity: Protects the elastomer body from mechanical damage, extending seal life. Compared to iron or plastic casings, stainless steel (typically 304, 316L) offers superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for humid or mildly corrosive environments.
-
Main Sealing Lip (with Garter Spring): The Heart of Sealing
- Function: Located on the inner side of the seal, it makes direct contact with the rotating shaft, primarily preventing the outward leakage of internal media (lubricating oil/grease).
- Structure: Made of elastomeric material, featuring a circumferential garter spring (typically a coiled stainless steel open ring) housed in a groove on its backside (air side).
- Critical Function of the Spring:
- Provides Continuous Radial Force: The spring continuously applies radial tension to the main lip, maintaining a constant radial contact pressure ("gripping force") against the shaft.
- Dynamically Compensates for Wear and Relaxation: This is the decisive value of the spring. During operation, the main lip elastomer wears down due to friction and experiences stress relaxation (loss of elasticity) under heat/pressure. The spring force automatically compensates for this material loss and reduced elasticity, maintaining tight lip-to-shaft contact and preventing premature leakage.
- Adapts to Shaft Runout/Eccentricity: The spring allows the main lip to conform to minor shaft movements (eccentricity, runout), preserving an effective seal.
- Ensures Low-Pressure Sealing: When system pressure is low or zero (e.g., startup, shutdown), the spring's radial force becomes the primary mechanism preventing media seepage.
- Design Goal: Achieve reliable, long-lasting dynamic media sealing, handling internal media pressure (typically low, relying mainly on spring + contact pressure) and managing friction-induced heat.
-
Secondary Dust Lip: The Barrier Against External Invasion
- Function: Positioned on the outer side of the main sealing lip (facing the external environment), it prevents ingress of external contaminants (dust, dirt, moisture, grit).
- Structure: Made of the same (or sometimes different) elastomer material as the main lip, typically without a spring.
- Operating Principle:
- Initial Contact & Scraping: Maintains slight preload contact pressure (lower than the main lip, relying mainly on elastomer elasticity).
- Physical Barrier: Forms a "gutter" (dirt exclusion groove between the two lips) that scrapes off and traps contaminants traveling along the shaft surface. Contaminants are held in the groove or expelled.
- Protects the Main Lip: This is the ultimate purpose. By shielding the primary sealing lip from abrasive external debris, it significantly reduces wear and damage, effectively extending the life of the main lip and the entire seal.
Overall Advantages of the Double-Lip Design:
- Dual Protection: Main lip retains oil/internal fluid, dust lip excludes contaminants – provides "inside-out and outside-in" defense.
- Synergistic Enhancement: The dust lip protects the main lip, extending its life; the casing provides stability; the spring ensures consistent lip performance. Synergy improves overall sealing reliability and longevity.
- Broad Applicability: Classic structure suitable for diverse scenarios, especially environments with external contamination risks.
- Proven Reliability: A long-standing industrial solution with stable, predictable performance.
II. Core Material Selection & Performance Comparison
Seal performance is highly material-dependent. Material selection differs by component (lips, casing). The casing is clearly stainless steel (304/316L). Lip material selection depends on the operating conditions:
| Lip Material |
Key Performance Characteristics |
Typical Application Fields |
| Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
Excellent resistance to mineral oils, lubricants, gasoline; Good abrasion resistance; Low cost; Limited temp. range (-30~100°C); Moderate ozone/weathering resistance |
Automotive/Agricultural wheel bearings, gearboxes; General industrial equipment; Pumps (mild env.) |
| Fluoroelastomer (FKM) |
Outstanding high-temp. resistance (≈-20~250°C); Exceptional resistance to fuels/oils/chemicals/solvents; Excellent ozone/weathering resistance; Low compression set (some grades) |
Automotive engine crankshaft/front/rear seals, turbochargers; Chemical pumps, high-temp fan bearings; High-temp equipment |
| Acrylate Rubber (ACM) |
Good resistance to hot oils/gear oils/ATF (≈-25~175°C); Excellent ozone resistance; Poor low-temp./water/ester solvent resistance |
Automotive driveline (transmission side shafts, axle shafts); Construction machinery driveline; Differentials |
| Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR) |
Superior abrasion resistance/strength/hot oil resist. vs. NBR (-40~150°C); Oil resistance similar to NBR; Excellent ozone/weather resistance; Higher cost than NBR |
High-speed, heavy-duty gearboxes, automotive A/C compressors; Demanding applications requiring upgrade from NBR |
| Silicone Rubber (VMQ) |
Extremely wide temp. range (-60~225°C); High elasticity/Low compression set; Excellent insulation/weather resistance; Poor oil/solvent resistance; Low strength |
Food/Pharma equipment bearings, high-speed/low-load seals, high-temp fans/motors, Cryogenic equipment |
- Selection Considerations: Prioritize primary media compatibility (oil, grease, fuel, chemicals), operating temperature range, and wear resistance requirements. Cost and environmental factors (e.g., food grade) are also important. The dust lip material is usually the same as the main lip, or sometimes a more wear-resistant/cost-effective option.
III. Typical Application Areas
Thanks to its effective "sealing + exclusion" dual-barrier design, reliable spring energization, and rigid casing support, the double-lip oil seal is widely used in harsh environments prone to dust, mud, water splash, and grit contamination:
- Automotive & Transportation:
- Wheel hub bearing seals (classic dust/water exclusion application).
- Engine: Crankshaft front/rear main seals (require high-temp/oil resistance), camshaft seals.
- Transmission/Drivetrain: Input/output shaft seals, axle shaft seals.
- Steering systems, Drive axles/Differentials.
- Construction & Agricultural Machinery:
- Final drives, swing bearings, hydraulic motor shafts on excavators, loaders, bulldozers (exposed to dirt, mud, water).
- Undercarriage bearings, driveline shafts on tractors, harvesters (high dust/mud environments).
- Industrial Equipment:
- Industrial fan/blower bearing housings (especially dusty environments).
- Pump shaft seals (exposed to moisture).
- Gearbox/Reducer input/output shaft seals.
- Mining machinery bearings (extreme dust, impact).
- Paper mill, Steel plant equipment (heat, moisture, dust).
- Others:
- Small electric motor shaft extensions.
- General transmission components requiring bearing protection from contamination.
Conclusion
The double-lip oil seal (spring-energized main lip + dust lip + stainless steel casing) achieves the dual goals of internal media containment and external environmental protection through well-defined structural roles: the casing stabilizes the form, the spring drives dynamic compensation of the main lip, and the dust lip forms the exclusion barrier. Understanding the design intent and functional boundaries of each part – particularly the spring's continuous compensation for wear/relaxation and the dust lip's critical role in shielding the main lip from abrasive wear – along with the correct selection of lip material (NBR, FKM, ACM, HNBR, VMQ) based on actual conditions (media, temperature, contamination level) is paramount to ensuring reliable long-term performance in diverse rotary sealing applications. This mature and effective design remains a vital sealing solution for safeguarding equipment operation in challenging environments.
[DLSEALS kindly Reminder] Sealing issues? Turn to DLSEALS! As a sealing component manufacturer, we specialize in customizing sealing components, providing a full range of services from design, research and development, production, testing, and more. If you have more information you'd like to know, feel free to contact us directly. DLSEALS's product experts are dedicated to serving you!
